Urological surgeons
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) is the most common method for treating an enlarged prostate. In this procedure, excess prostate tissue is removed through the urethra (without the need for an external incision) to improve urine flow.
Transurethral Prostatectomy (TURP): Possible complications include bleeding, infection, TURP syndrome (related to fluid absorption during surgery), urinary problems (such as frequency or inability to void), urinary incontinence, sexual dysfunction (erectile dysfunction), retrograde ejaculation (semen entering the bladder), and urethral or bladder neck stricture.
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a procedure used for larger kidney stones or stones located in harder-to-reach areas, such as large kidneys or deep stones. In this method, the surgeon accesses the kidney through a small incision in the skin and removes the stone. This surgery requires general anesthesia.
Percutaneous Kidney Stone Surgery: Risks include bleeding, infection, pain, injury to nearby organs such as the bowel and liver, and anesthesia complications. Generally considered safe, with serious complications being rare.
A unilateral varicocelectomy is a surgery performed to treat varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum). In this procedure, only one side of the testicle (left or right) is operated on. Varicocele usually results from the enlargement of veins in the scrotal area, which can lead to issues such as pain, infertility, or a reduction in testicle size.
Unilateral Varicocele: Complications include infection, swelling, bruising, chronic pain, hydrocele (fluid accumulation around the testicle), injury to the testicular artery leading to testicular shrinkage, and recurrence
Bilateral varicocele refers to a condition in which the veins in both testicles (left and right) become enlarged. This issue can cause symptoms such as pain in the scrotal area, infertility, a reduction in testicle size, or impaired sperm production. In severe cases, bilateral varicocele may negatively affect a person’s fertility potential.
Complications Bilateral Varicocele: Risks include hydrocele, chronic testicular pain, recurrence, injury to the testicular artery (possible testicular shrinkage), as well as general surgical risks such as infection, bruising, swelling, and anesthesia complications.
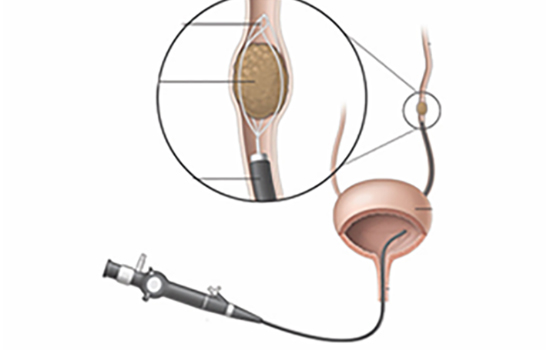
Intracorporeal Lithotripsy is a non-surgical method used to treat kidney, ureter, or bladder stones. In this procedure, instead of an external incision, stones are broken from within the body
Complications Ureteroscopy (Endoscopic Stone Removal): Common risks include mild bleeding and flank pain during urination. Less common but more serious risks include urinary tract infection, ureteral stricture, and possible injury to the urinary tract. Stent use may cause discomfort and urinary frequency. Passing stone fragments may be painful and cause nausea.
Hypospadias Surgery is a procedure performed to correct congenital abnormalities in the location of the urethral opening on the male genitalia. The primary goal of this surgery is to restore the natural position of the urethral opening at the tip of the penis and correct any curvature in the penis. Hypospadias occurs when the urethral opening is located in an abnormal position, lower than its usual place.
Complications Hypospadias Repair: Complications include urinary fistula (urine leakage from the surgical site), urethral stricture (narrowing requiring dilation or re-surgery), wound dehiscence, wound infection, and penile curvature during erection.
